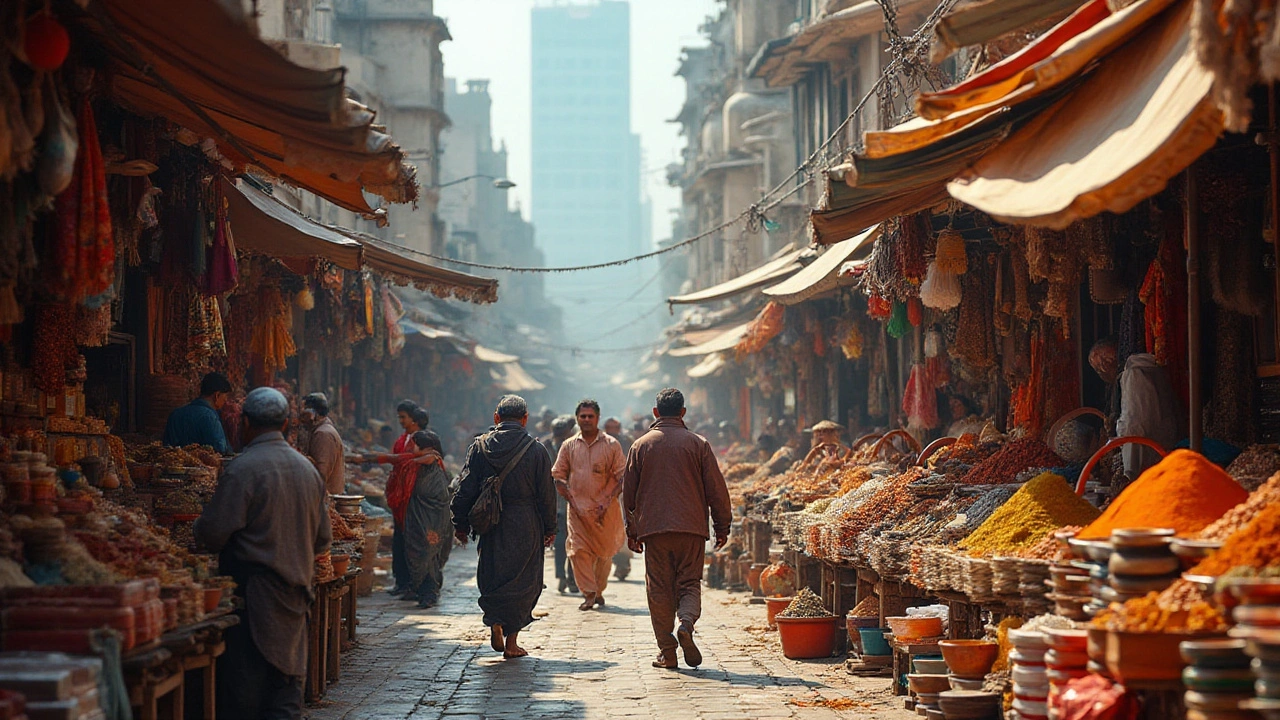
India, with its vibrant culture and vast history, stands as a country of immense potential and diversity. When we consider the question of whether India is rich, the answer isn't a simple yes or no. Instead, it opens up a discussion about economic indicators, opportunities for growth, and the challenges that the country faces.
In recent years, India has seen a surge in economic development and globalization's impact on its markets. The emergence of trade courses has been significant in this transformation, offering skills that cater to the sectors fueling economic growth. These courses empower individuals with technical knowledge, playing a vital role in strengthening the workforce.
However, despite progress, disparities exist, and India continues to grapple with issues such as poverty and infrastructure deficits. Understanding if India is rich involves examining this intricate balance between prosperity and the hurdles that still exist. Through an exploration of economic data, policy impacts, and educational advancements, we can better understand India's position on the global economic stage and its journey towards sustained wealth.
- Defining Richness in the Indian Context
- Economic Indicators and Growth Rates
- The Role of Trade Courses in Economic Growth
- Challenges Facing India's Wealth
- Future Prospects and Global Positioning
Defining Richness in the Indian Context
The term 'richness' often brings to mind images of wealth, abundance, and opulence, yet in a country as vast and varied as India, its definition takes on multiple interpretations across its states and communities. India, known for its significant contributions to global history and culture, stands as the world's fifth-largest economy by nominal GDP. However, when evaluating its richness, it's crucial to consider not just economic statistics but the multidimensional factors such as cultural heritage, natural resources, and human capital.
India's economic wealth has steadily grown over the past decades. According to the International Monetary Fund, India's GDP growth rate averaged over 7% between 2014 and 2018, representing one of the fastest-growing major economies globally. This growth, propelled by sectors like technology, pharmaceuticals, and automotive, has created a middle class larger than the population of many countries, contributing to the perception of India's wealth. Yet, economic wealth only scratches the surface.
Consider the richness of diversity seen in India's cultural fabric. With over 2,000 distinct ethnic groups and more than 1,600 spoken languages, cultural richness stands as a testament to the country's historical opulence, inviting researchers and travelers alike. From the bustling streets of Mumbai to the serene landscapes of Kerala, the richness extends beyond economic figures into the realms of art, religion, and lifestyle.
Yet, challenges persist. Issues such as income inequality and poverty paint a different picture when assessing wealth. According to the World Bank, despite advances, a significant portion of the population remains below the poverty line. This duality—of burgeoning economic power and profound socioeconomic challenges—adds layers to understanding what 'richness' means for India today.
"Without addressing the wide gaps in economic opportunity across its populace, India's story remains incomplete." - Dr. Amartya Sen, Nobel laureate economist
Additionally, India's role in global trade has been pivotal. The share of India's exports to global trade as a percentage of GDP has been significant in driving economic growth, with trade courses now sharpening skills required for flourishing industries. These courses have strengthened sectors like IT, textiles, and machinery, making India a competitive player on the world stage.
In sum, defining richness within the Indian context requires a holistic view that transcends traditional financial metrics to incorporate cultural, educational, and structural elements. This comprehensive understanding seeks to align economic growth with human development, recognizing that the true wealth of a nation lies in the capability of its people to thrive in bearing strategies that nurture and sustain future prosperity.
Economic Indicators and Growth Rates
The economic journey of India has been nothing short of remarkable, fueled by a potent combination of policy reforms, technological advancements, and demographic youth-driven energy. Understanding India's wealth status involves dissecting its economic indicators and the intricate patterns of its growth rates. A stroll through its economic landscape reveals not just statistics but stories of resilience and potential.
India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) provides a substantial part of this narrative, marking India as one of the largest economies globally. A consistent growth rate hovering between 6% to 7% over recent decades makes India an attractive market for global investors. With a GDP value surpassing $3 trillion as of the last fiscal assessment, the country is making its mark. However, it's pivotal to note that GDP growth, while significant, doesn't necessarily equate to uniform richness. The wealth distribution in India presents a mixed picture. Urban pockets such as Mumbai and Bengaluru bask in opulence, whereas rural regions still wrestle with economic challenges.
As per the World Bank, India's growth has been remarkable, yet the depth of its influence varies across multiple sectors and geographies. “India's growth prospects are bright, yet its challenges remain significant,” states an analysis from the International Monetary Fund. This statement highlights that understanding India's wealth involves not just looking at the figures but appreciating the underlying intricacies.
Inflation is another crucial economic indicator, which India's economy has tackled with varying success. Inflation rates, which climbed to concerning heights previously, have seen a moderate downward trend due to decisive monetary policy actions. This stabilization contributes positively to enhancing consumer confidence and stabilizing purchasing power, which are central to long-term growth.
Investments in infrastructure and technology also serve as growth harbingers. The government's initiatives in boosting transport and digital infrastructure, such as the 'Digital India' initiative, play a monumental role in pushing the economic envelope. These efforts accelerate India's goal of becoming a formidable player on the global stage, fortifying trade and commerce along the way. Yet, the persistent issue of income inequality plays spoil-sport to India's economic grandeur, emphasizing the need for targeted financial and social interventions.
Labor and productivity metrics also form an essential component of the economic assessment. While India boasts a massive labor force, skill gaps and unbalanced deployment pose challenges. Here, trade courses designed to impart specialized skills are vital, aligning human capital with industry needs. By coalescing education and employment, India looks to bridge these gaps, enhancing productivity and inclusive growth.
“Harnessing India's demographic dividend requires strategic implementation of skill development and economic inclusivity,” suggests a report by NITI Aayog, India's principal policy 'Think Tank'.
In sum, the tapestry of India's economic story is woven with threads of both promise and hurdles. As we assess these economic indicators, it's clear that while tangible growth is evident, the path to a uniformly rich India calls for sustained efforts in policy, education, and innovation. Only then can the dream of a truly wealthy India come to fruition, benefitting not just a few but all sections of its diverse populace.

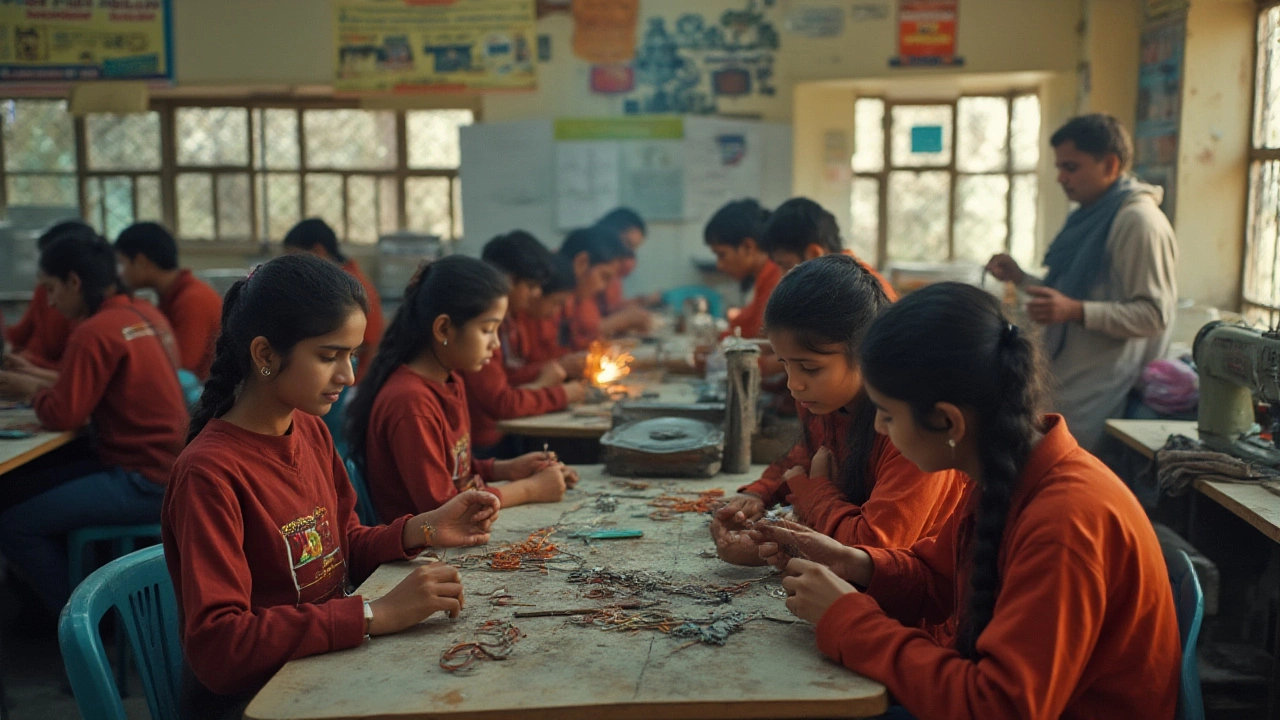
The Role of Trade Courses in Economic Growth
In a country as diverse and expansive as India, education plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape. Trade courses, in particular, have emerged as critical pathways for economic development. These courses bridge the gap between basic education and the specific skills demanded by thriving industries. The economic benefits of such courses are multi-fold, manifesting not only in individual growth but also in enhanced national productivity. Trade courses equip students with skills that are directly applicable to various industries, from manufacturing to information technology. This direct applicability means graduates can quickly adapt to workplace requirements, minimizing training costs for businesses and reducing the time taken to achieve productivity.
The rise of trade education has paralleled shifts in India's industrial landscapes, which increasingly demand specialized skills. With the Indian economy's pivot to more technical and technologically-driven domains, trade education acts as both a catalyst and a foundation for sustainable growth. Approximately 60% of India's population is under 35 years old, marking it as one of the youngest countries globally. This demographic dividend presents an opportunity but also necessitates targeted skills training. By aligning trade courses with industry needs, India can harness this youthful energy to drive economic growth.
Importantly, the focus on trade education extends beyond urban facilities into rural areas. Access to quality education in these regions can significantly narrow economic disparities across the country. According to a report by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO), there is a higher return on investment in skills development in rural regions compared to urban settings. This is an area where policy initiatives have aimed to improve access to and quality of trade courses, recognizing their potential to bolster rural economies.
Highlighting the value of these courses, a study from the World Bank stated, "Investment in vocational training and education significantly contributes to economic growth and poverty alleviation in emerging economies."
Programs like Skill India aim to standardize and proliferate trade courses across the nation, setting benchmarks for quality and result-oriented education. The diversity of courses—from electrical and plumbing to fashion design and computer programming—reflects the wide spectrum of sectors fueling the economy. By encouraging collaborations between educational institutions and industries, these programs ensure that trade education remains relevant and future-oriented.
The success of trade courses is evident in the higher employability rates for students who opt for these career paths. According to data from the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, graduates of trade courses in India tend to secure employment more rapidly compared to their peers from conventional academic tracks. Offering practical training and real-world problem solving, these programs foster not just employment, but innovation and entrepreneurship as well.
Challenges Facing India's Wealth
India's journey towards becoming a truly wealthy nation is laden with challenges woven intricately into its societal fabric. One of the primary obstacles is its demographic diversity. The vast population, while a potential demographic dividend, places immense pressure on resources, employment, and infrastructure. With over a billion people striving for better living standards, the gap between urban and rural areas creates economic disparities that are difficult to bridge. Urban centers have surged ahead, enjoying prosperity and technological advancements, while rural regions often lag, lacking basic amenities. The challenge is addressing these disparities effectively.
Another significant hurdle is the infrastructure deficit. Despite notable progress in urban development, many regions still suffer from inadequate transport facilities, unreliable power supply, and insufficient water resources. This not only hampers everyday life but also affects industries reliant on consistent infrastructure for smooth operations. As an economy aspiring for a larger global footprint, this infrastructural inadequacy can be a limiting factor. A well-planned investment in infrastructure, focusing on both urban and rural areas, is crucial for unlocking India's full economic potential.
The educational landscape also requires close attention. While India has made strides in providing access to education, the quality remains uneven across the country. A strong economic status is often built on an educated workforce; however, many educational institutes do not equip students with the necessary skills for the modern job market. Trade courses offer a promising avenue to bridge this gap by providing practical skills and driving employment opportunities in burgeoning sectors. There's a critical need for government policies and private investments to support these initiatives to uplift skill levels nationwide.
Economic policy and regulatory challenges also affect India's wealth trajectory. The business environment, although improving, still faces bureaucratic obstacles and complex tax laws that can deter foreign investment. Simplifying procedures and fostering a more business-friendly atmosphere can significantly enhance India's economic wealth. Moreover, corruption, though reduced, continues to siphon resources meant for development projects. Ensuring transparency and accountability within governance structures is essential for sustainable progress.
The environmental impact of economic growth presents another formidable challenge. Accelerated industrialization and urbanization have led to pollution and resource depletion, threatening both health and sustainability. India must balance its developmental goals with environmental preservation. Implementing green technologies and sustainable practices will be critical in addressing these concerns while still pursuing economic expansion. Climate change and its implications on agriculture, which employs about half of the workforce, add another layer of complexity to India's growth strategy.
Aside from these logistical and systemic issues, socioeconomic factors like poverty and inequality continue to weigh heavily on India's prosperity. Addressing income inequality and ensuring access to basic services across different strata of society is imperative for achieving genuine richness. Economic policies must aim to create equitable growth that uplifts the marginalized and brings holistic welfare. With a strategic approach tackling these challenges, India can truly harness its abundant resources, human and mineral, and translate them into sustainable wealth for all its citizens.

Future Prospects and Global Positioning
The intricate dance that shapes India's future prospects lies in its strategic positioning on the global economic stage. With a billion-strong population and a burgeoning middle class, India stands at the cusp of a significant transformation. This demographic advantage, often referred to as the 'demographic dividend,' offers both challenges and unparalleled opportunities. As the world looks towards emerging economies, India's role becomes increasingly pivotal. Economists predict that if India capitalizes on its youth, channeling their energies into productive avenues through education and employment, the country could potentially outpace the growth trajectories of established economies. Trade education and skill development initiatives are paramount in this journey, providing the necessary tools for the workforce to thrive in various sectors, including technology, manufacturing, and services.
India's GDP has seen substantial growth over the decades, supported by reforms that have liberalized the economy. However, sustainable development remains crucial. With global trends shifting towards green energy and digital transformation, India has been investing in renewable resources and technological innovations. The government's emphasis on 'Make in India' and 'Digital India' initiatives are intended to boost manufacturing prowess and digital infrastructure. This strategic development could elevate India's position as a preferred outsourcing destination and a manufacturing hub. Reports from the World Bank suggest that India could become the third-largest economy by 2030 if these strategic plans are implemented effectively.
"India's potential to navigate its demographic advantage into economic prosperity depends significantly on its ability to spur education and create infrastructural ecosystems," opined Shashi Tharoor, an esteemed Indian politician and author.Yet, challenges like inequality, inadequate infrastructure, and policy implementation hurdles remain formidable. To address these, India must not only invest in economic growth but also focus on inclusive wealth distribution. Equitable growth could bridge existing gaps, fostering a conducive environment for business and innovation. The country's focus on trade courses plays a significant role in equipping the workforce with practical skills necessary to adapt to changing trade dynamics, further reinforcing India's capability to compete globally.
A look at India's economic alliances underscores its strategic foresight in global positioning. India is aligning with global superpowers, nurturing trade relationships through organizations such as BRICS, G20, and international trade pacts. This collaboration is not just about economic gains; it reflects a desire for a more significant, responsible role in global decision-making. With looming geopolitical shifts and supply chain realignments post-pandemic, India's adaptability and growing influence could catalyze its emergence as an economic powerhouse of the 21st century. The optimism surrounding India's growth trajectory is palpable, yet this ascent is contingent on sustained efforts, continued policy support, and a relentless focus on innovation and inclusivity.